DO NOT USE - ALL INFORMATION LIKELY INCORRECT IF NOT ACTIVELY DANGEROUS
Please use current guidelines available on the UHNM intranet for patient treatment
Please use current guidelines available on the UHNM intranet for patient treatment
RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
Symptoms and signs
- Various CNS symptoms e.g. lethargy to coma and seizures
- Dehydration - hypovolaemia
- Those of underlying cause
Clinical Assessment
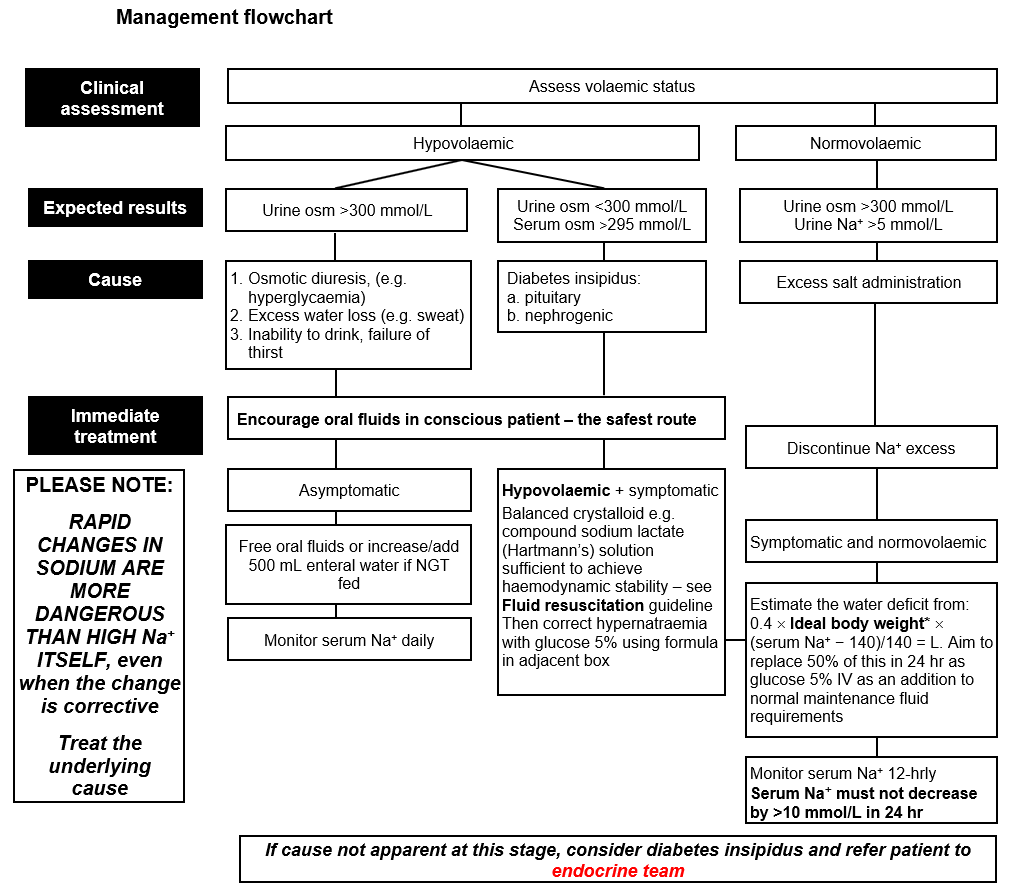
- Assess volaemic status
Investigations
- Serum: U&E, glucose, osmolality
- Urine: U&E, osmolality
RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
- Treat the underlying cause. For guidance follow flowchart
- If cause still not apparent, consider diabetes insipidus and refer patient to endocrine team
Sodium Levels
- Rapid changes in sodium are more dangerous than HIGH Na+ ITSELF, even when the change is corrective
- Serum Na+ must not decrease by >10 mmol/L in 24 hr
Last reviewed: 2024-03-06