DO NOT USE - ALL INFORMATION LIKELY INCORRECT IF NOT ACTIVELY DANGEROUS
Please use current guidelines available on the UHNM intranet for patient treatment
Please use current guidelines available on the UHNM intranet for patient treatment
RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
- Parkinson's Disease (PD) is characterised by:
- tremors, rigidity, akinesia, postural instability
- decline in swallowing function
- neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- range of non-motor complications (e.g. psychiatric and sleep disorders)
History
- Take an accurate drug history
- know precisely how PD is managed by patient
- taking their normal doses in recent days (e.g. too unwell to take as normal)?
- Consider all sources of information including:
- patient, usually well informed on their precise treatment
- summary Care Records/GP fax/GP phone call/previous TTO
- carer(s)/next of kin
- transferring hospital/nursing home/residential home prescription charts
- patient's own drugs (PODs)/repeat prescriptions
- computer letters and notes
INITIAL MANAGEMENT
- If possible, continue patient's individualised PD treatment
- Discuss with a PD specialist whether dose adjustments may be required
- Prescribe all PD medications, specifying exact timings as necessary
- e.g. co-beneldopa 12.5/50 mg 6-hrly; 0600, 1000, 1400, 1800
- ensure supply of required PD medications are available
- Do not stop or miss doses of levodopa or dopamine agonists
- prescribe COMT inhibitors (e.g. entacapone) at the same time as levodopa-containing medicines
- Avoid medicines which may worsen PD
- antipsychotics (haloperidol). If necessary, consider a benzodiazepine
- anti-emetics (metoclopramide and prochlorperazine). If necessary, consider domperidone (if nausea not transient, think ECG QTc prolongation)
Nil-by-mouth or compromised swallow
- Refer for urgent swallowing assessment
- Consider placing tablets on a teaspoon with thickened fluids/soft foods (e.g. yoghurt), or dispersible/liquid preparations
- Check for underlying cause and treat accordingly
- COMT inhibitors and MAOB inhibitors can be safely omitted temporarily
- If already using apomorphine injection or infusion, continue current regimen
- do not initiate apomorphine without involvement from a PD specialist
Patient not able to take next oral dose
- Priority: maintenance of dopaminergic medication
- Refer patient to PD specialist and swallowing team ASAP. If unable to contact (e.g. out-of-hours):
- if NG tube placement possible, give via enteral feeding tube at usual times. For advice on doses via enteral feeding
- if NG tube placement impossible, convert to equivalent dose of rotigotine patch. For advice on dose of rotigotine patch
Apomorphine
- If already using apomorphine, continue current regimen
- Do not initiate apomorphine without involvement from a PD specialist
- APO-go (apomorphine) 24 hr helpline
- 0844 8801327 (www.apo-go.com) hcp
Rotigotine patch administration
- For advice on dose of rotigotine patch
- Apply patches once a day. Press firmly on back of patch for a minimum of 30 seconds onto skin to activate adhesive - see Figure 1
- Apply patch at approximately the same time each day
- ensure old patch is removed. Use Transdermal Patch Body Map
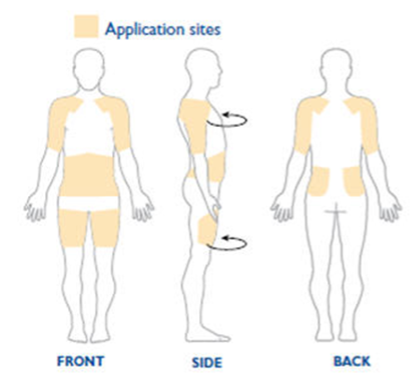
- Rotate application site daily to reduce risk of skin irritation (do not use same area of skin again for 14 days). See Figure 2 for suggested application sites
Monitor patient
- 4-hrly observations including
- sedation
- respiratory rate
- application site
- response
- If increased stiffness/slowness, increase dose and review daily
- If increased confusion/hallucinations, decrease dose and review daily
SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT
- Decided by PD specialist
Last reviewed: 2024-03-14